RECOMMENDED VIDEOS

Bullfrog Power - Green Natural Gas: How it Works
Bullfrog Power

Introduction of Biogas digester - The Little Green Monster
ENERGYWEB Stella Weber

Inverpower : Distributing ABB Solar Inverters From Micro…
InverPower Sdn Bhd

Span Pumps (India) : Kalpa Power's Efficient Auto-cleaning…
Span Pumps Pvt. Ltd

Yingli Solar Powers 8MW Kompleks Hijau Solar Plant in Malacca,…
Yingli Green Energy Holding Co., Ltd.
Related Stories
The largest solar farm apiary in the US opens this week
New study suggests that plastic waste may be transformed into usable energy
Uravu’s zero-electricity Aqua Panels produce gallons of water from thin air
104% of Portugal’s electricity consumption in March came from renewable energy
Germany Sets New Solar Record By Meeting Nearly Half of Country’s Weekend Power Demand
16 Nov, 2016

Tiny power plant sucks CO2 from the air and turns it into fuel
Renewable Energy & Energy Efficiency | FINLAND | 16 Nov, 2016
Published by : Eco Media Asia
Ineratec, an offshoot of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), has devised a creative solution to the excess carbon dioxide (CO2) soaking the atmosphere. The company developed a small power plant that sucks CO2 out of the air and turns it into fuel. Researchers aim to switch on a pilot plant, called the Soletair Project, at the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland later this year.
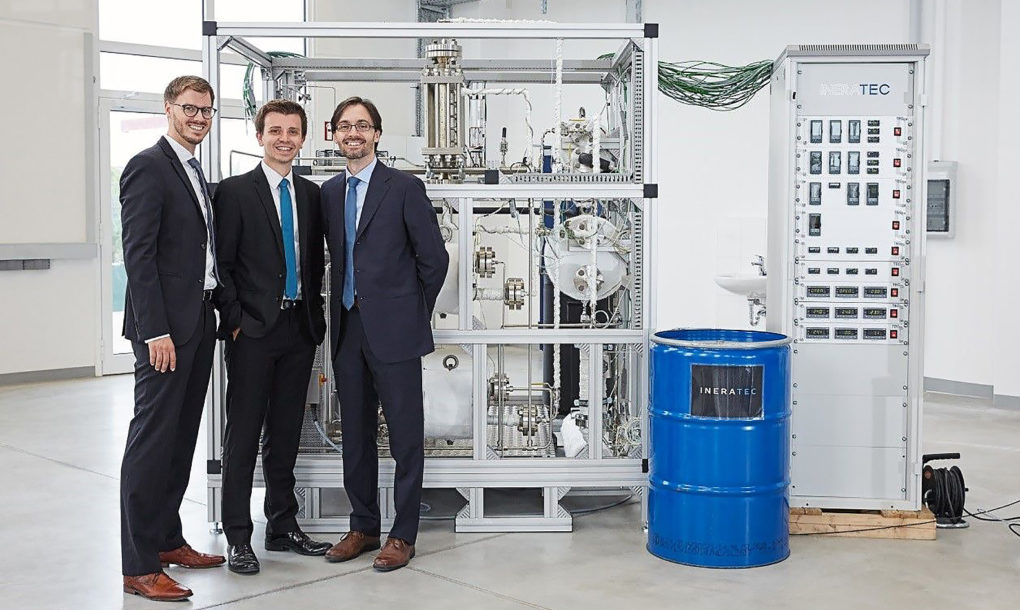
Ineratec’s mini power plant is so small it can fit inside a shipping container. KIT says there are three parts to the system: a microstructured reactor, a direct air capture unit created by VIT, and an electrolysis unit which runs on solar power created by Lappeenranta University of Technology (LUT). The direct air capture unit extracts CO2 out of the air and then the reactor converts the CO2 and regenerative hydrogen via the electrolysis unit into fuel. The Ineratec founders say the system can produce gasoline, kerosene, or diesel.
Ineratec founder Tim Böltken told New Atlas, “We supply an entirely new, modular technology that is a real alternative to the costly large chemical facilities used for the conventional gas-to-liquid process.” Böltken said there are many other possible applications for the plant, including gathering fuel from sewage treatment facilities. He also suggested organic farmers might be able to use the system to generate energy.
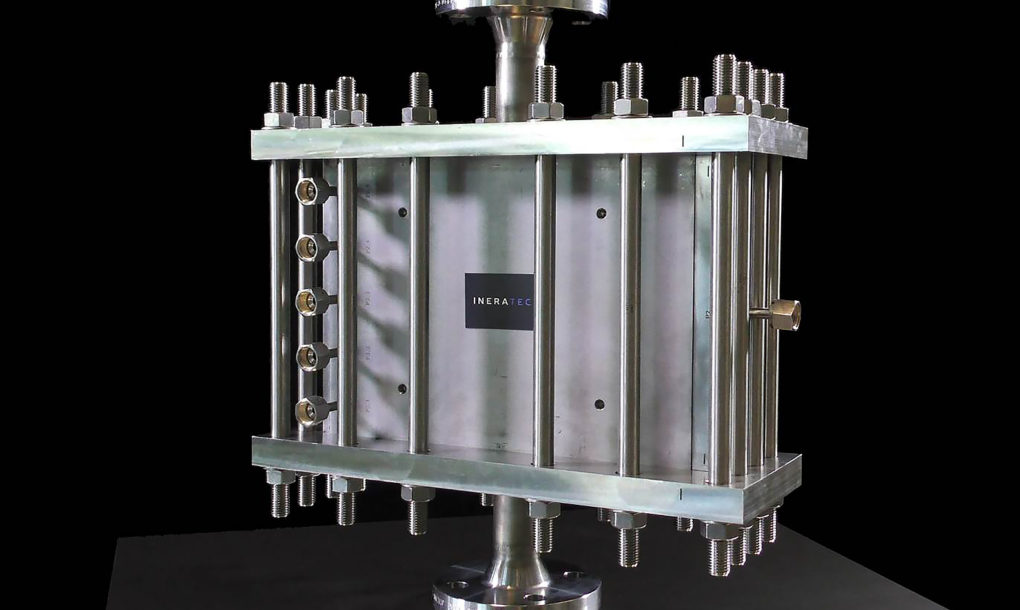

VTT Principal Scientist Pekka Simell said in a statement, “The project will produce expertise for enterprises in various fields, and it will result in a multidisciplinary industrial integration that no one company can achieve on its own.”
VTT and LUT will build a demonstration plant set to being operating this year, and in 2017 LUT plans to continue testing. According to KIT, Ineratec is planning to commercialize the compact plant, which could hit the market in 2018.
